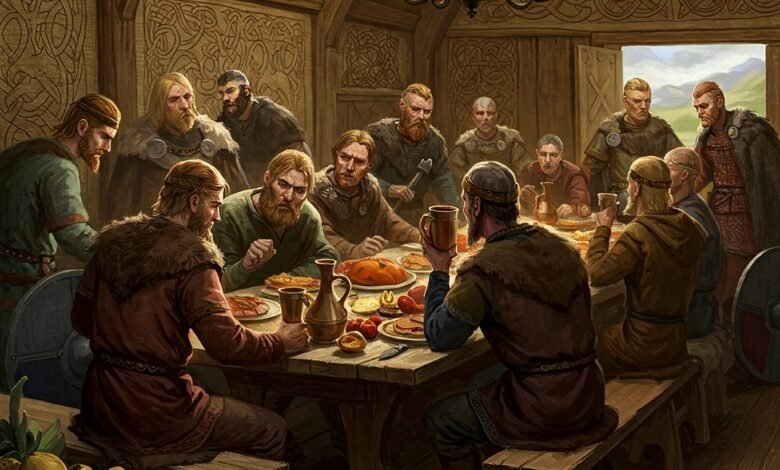
Introduction to the Vikings
The Vikings, a seafaring people from the late eighth to early eleventh century, originated primarily from the Scandinavian regions of Norway, Sweden, and Denmark. This era, commonly referred to as the Viking Age, spanned from approximately 793 to 1066 AD, marked by a series of expeditions that saw the Vikings engage not only in raiding but also in exploration and trade. Contrary to popular belief, the image of the Vikings as mere ruthless warriors does not encompass the full scope of their multifaceted society.
The geographical reach of the Vikings extended far beyond their homelands. They navigated the waters of the North Atlantic, establishing settlements in places such as Iceland, Greenland, and even reaching the shores of North America, specifically an area known as Vinland, believed to be located in modern-day Newfoundland. In addition, their exploratory ventures took them down the rivers of Eastern Europe, penetrating as far as the Byzantine Empire and the Middle East. This extensive network facilitated not only military campaigns but also a vibrant trade system that connected various cultures and economies.
Origins and Settlement
The Viking Age, which spanned from approximately 793 to 1066 AD, is often characterized by the seafaring endeavors of the Norse people from the Scandinavian regions of Denmark, Norway, and Sweden. These geographic areas were inhabited by various tribes who shared a common linguistic and cultural heritage, which contributed significantly to their collective identity as Vikings. Their origins can be traced back to the early Germanic tribes, with a rich tapestry of mythological and historical narratives providing context for their development.
Initially, these Norse tribes practiced agriculture and animal husbandry, focusing on subsistence living. However, as population densities increased and resources became scarce, many communities began to look beyond their borders. This shift marked the beginning of their maritime expansion, facilitated by advancements in shipbuilding technology, particularly the iconic longship, which enabled them to navigate both open seas and shallow rivers. This technological innovation was pivotal in establishing the Vikings as a formidable maritime presence throughout Europe.
Settlements emerged as these seafaring communities established trade routes and explored new territories, leading to the establishment of Viking colonies in places such as Greenland, Iceland, and Newfoundland. Furthermore, the Vikings created trading centers, like Birka in Sweden and Hedeby in Denmark, which became hubs of commerce connecting them to various cultures across Europe and the Mediterranean. Through these interactions, they exchanged goods, ideas, and innovations, illustrating their adaptability and entrepreneurial spirit.
Their societal structures were as complex as their explorations. With a focus on kinship, the Vikings maintained strong familial ties that dictated social hierarchies and communal governance. Chiefdoms often emerged, headed by local chieftains who guided their followers in both war and peace. This blend of community solidarity and valorous leadership was essential in the establishment of a distinct Viking identity, which would resonate throughout their history.
Viking Society and Culture
The Viking Age, spanning from approximately 793 to 1066 CE, was characterized by a distinct social structure and rich cultural practices. Viking communities were organized into clans or kinship groups, which formed the backbone of their social life. These groups provided mutual support, cooperation, and shared identity, often centered around a chieftain or leader who held authority and made critical decisions concerning the clan’s welfare.
In terms of gender roles, Viking society was patriarchal; men primarily engaged in raiding, trading, and farming, while women were responsible for managing the household, which included tasks such as weaving and food preparation. However, women’s rights were relatively advanced for the time. They had the ability to inherit property, request divorce, and maintain their independence within the household. Children in Viking society were also valued, participating in various family and community activities, preparing them for adult responsibilities.
Central to Viking culture were their beliefs in a pantheon of gods, known for their complexity and variability. Polytheism played a significant role in daily life, with deities such as Odin, Thor, and Freyja being worshipped and revered. These gods symbolized different aspects of life and nature, influencing everything from agriculture to warfare. Additionally, the practice of storytelling was pivotal; sagas and myths served to educate, entertain, and reinforce cultural values. These narratives often revolved around heroic deeds, the supernatural, and moral lessons, ensuring the preservation of Viking identity across generations.
Customs and laws were also vital in Viking culture, with many aspects codified in early legal texts. The Thing, an assembly that convened to resolve disputes and make communal decisions, exemplified early democratic principles. Overall, Viking society was a complex tapestry of customs, beliefs, and social structures that significantly influenced their legacy in history.
The Viking Age: Exploration and Expansion
The Viking Age, spanning from approximately 793 to 1066 AD, represents a significant period marked by the Norsemen’s maritime prowess and expansionistic spirit. This era commenced with the infamous raid on the monastery at Lindisfarne in 793, a significant event that shocked the Christian world and signaled the onset of Viking incursions across Europe. Over the following centuries, the Vikings embarked on extensive raids that targeted coastal towns, monasteries, and trade routes, significantly impacting the regions they encountered.
One of the primary factors contributing to the Vikings’ remarkable success in exploration and expansion was their advanced shipbuilding technology. The longships, characterized by their clinker-built design and shallow drafts, allowed the Vikings to traverse both open oceans and shallow rivers ineffectively. This innovative marine technology facilitated long-distance travel, enabling the Norsemen to reach as far west as North America, as evidenced by the Viking settlement at L’Anse aux Meadows, and to the east into Russia, where they established trade routes along major river systems.
The Viking expeditions were not solely aggressive; they also led to significant cultural exchanges. As Vikings interacted with various societies, they assimilated influences from European, Byzantine, and Islamic cultures. These exchanges contributed to a rich tapestry of cultural development, resulting in advancements in trade, art, and governance within Viking communities. The establishment of trade networks fostered economic prosperity, as goods such as furs, amber, and silver circulated across the continent, further intertwining the Norse with other societies.
Moreover, the expansion of the Viking Age included settlement endeavors, exemplified in the establishment of territories such as Danelaw in England and settlements in Ireland and Iceland. These actions laid the groundwork for future generations, influencing the sociopolitical landscapes of these regions and echoing Viking legacy throughout history.
Trade and Economy
The Viking Age, spanning from the late 8th century to the early 11th century, was marked by a significant expansion of trade and economic activities that had far-reaching implications not only for the Norse people themselves but also for the regions they engaged with. Viking traders established extensive networks that connected them to various markets across Europe, the Middle East, and even the Americas, reflecting their sophisticated understanding of commerce and economic relationships.
A variety of goods were exchanged in these trading ventures. The Vikings were known for their production and trade of high-quality items such as furs, timber, iron, and ornaments made from silver and gold. These commodities were not only valuable in their own right but also facilitated trade with other cultures, allowing the Vikings to acquire spices, silk, glassware, and other luxury items that were highly sought after. This dynamic exchange contributed significantly to the wealth accumulation of Norse societies, enabling further exploration and expansion.
Viking traders often used a system of currency that included silver coins, ingots, and even abarther coins from the lands they interacted with, such as Arabic dirhams and Byzantine solidi. This form of currency enhanced their trading capabilities and made transactions smoother across diverse cultures. The practice of using coins was not just a mechanism of trade; it also played a role in the Vikings’ interactions with other populations, fostering relationships built on economic ties.
In addition to tangible goods, the Vikings’ trade networks served as conduits for cultural exchange and information dissemination. As they interacted with different peoples, they absorbed new ideas, technologies, and practices that enriched their own culture. The interconnectedness fostered through trade contributed to the overall development of Viking society, making it a significant aspect that deserves recognition when studying their history.
Viking Raids and Warfare
The Viking Age, spanning from the late 8th to the early 11th century, was marked by a series of significant raids and military campaigns carried out by Scandinavian warriors. These expeditions were primarily motivated by the search for wealth, resources, and new territories. The Vikings, known for their seafaring skills, utilized longships that enabled them to traverse vast distances, reaching as far as the British Isles, the Iberian Peninsula, and even Constantinople.
Their strategies in warfare were both innovative and effective. Vikings often employed the element of surprise, launching raids during the early morning or at dusk when their enemies were least prepared. Their ability to strike quickly and retreat before significant resistance could be mobilized underpinned the effectiveness of their military tactics. Additionally, they often targeted monasteries and coastal settlements, which were perceived as rich in wealth and poorly defended.
Viking weaponry included a diverse array of arms that enhanced their combat effectiveness. Typical armaments comprised axes, swords, and spears, complemented by shields made from wood or hide. The famous Viking longship not only allowed for rapid transport but also facilitated beach landings, further contributing to their success in raids. Historical accounts indicate that due to their fierce reputation, the sight of a Viking ship instilled fear among potential targets, often leading to the looting of valuable resources without a fight.
Beyond their immediate impact on the areas they invaded, Viking raids significantly shaped the socio-political landscape of Europe during the Middle Ages. These incursions contributed to the destabilization of several kingdoms, prompting them to develop more robust defenses and military alliances. The cultural exchanges that occurred during these raids, coupled with the establishment of trade routes, laid the groundwork for a complex interaction between the Viking culture and the regions they engaged with. Ultimately, the legacy of Viking raids extends beyond mere conquest, as it played a pivotal role in shaping European history.
Religious Beliefs and Practices
The religious beliefs of the Vikings were rooted in a complex system of mythology that revolved around a pantheon of gods and goddesses. Principal deities included Odin, the all-father and god of wisdom and war; Thor, the god of thunder and protection; and Freyja, the goddess of love and fertility. These figures were central to Viking beliefs and played pivotal roles in their understanding of the world. Consequently, their myths were not merely stories, but represented the values, ideals, and aspirations of Viking society.
Rituals and practices were equally integral to their religion. Vikings conducted various ceremonies, including sacrifices and offerings to deities, seeking favor in battles, bountiful harvests, and successful voyages. One of the most renowned rites was the blóts, wherein animals were sacrificed to honor the gods, their blood spilled as a means to communicate divine favor. Furthermore, feasts often accompanied these rituals, underscoring the communal aspect of Viking spirituality.
The symbols of Viking religion played a significant role in their daily lives, with runes and sigils carved into weapons, buildings, and jewelry believed to provide protection or blessings. One of the most potent symbols was the Valknut, which is associated with Odin and often interpreted as a representation of the afterlife and transition between worlds.
As the Viking Age progressed, a gradual transition from paganism to Christianity began to shape their society. This shift was marked by the gradual conversion of Viking leaders and subsequent influence on their subjects. The introduction of Christian beliefs led to the transformation of societal structures and traditions, ultimately influencing their customs and diminishing the prominence of their original religious practices. The juxtaposition of Viking pagan beliefs and the emergence of Christianity serves as a vital point of exploration in understanding the nuances of their culture and the legacy they left behind.
Art and Craftsmanship
The Vikings are well-known for their impressive artistic achievements, which reflect their rich culture and values. Among the most notable forms of Viking art are metalwork, wood carving, and textile production. Each art form serves as a testament to their skill and the importance of craftsmanship in their daily lives.
Viking metalwork showcases the advanced techniques of the era, with artisans creating intricate jewelry, weapons, and tools. Gold and silver were often adorned with elaborate designs, featuring animal motifs and interlacing patterns that tell stories of the Vikings’ mythology and beliefs. Such craftsmanship not only illustrated their skills but also communicated power and status, as these items were often worn by chieftains or depicted in burial rites, indicating the significance of adornments in social hierarchy.
Wood carving is another essential artistic expression among the Vikings. They expertly crafted longships and household items, such as chairs and bowls, which were typically embellished with detailed carvings of mythical creatures and scenes from daily life. The Vikings’ affinity for wood carving reveals their deep connection to nature and their surroundings while underscoring the importance of functionality in their artistic endeavors. The ships they built were not only practical for navigation but also stood as symbols of exploration and conquest, further enhancing their cultural impact.
Textile production also played a vital role in Viking society. Women primarily engaged in weaving, creating garments that were both practical and decorative. Intricate patterns and vibrant dyes reflected the individual’s social standing, with higher-status individuals often adorned in more elaborate designs. This art form encapsulates the daily life of the Vikings, as textiles were essential for warmth and practicality, showcasing their resourcefulness and creativity. Furthermore, Vikings exported their textiles, influencing the material culture of the regions they settled, thus leaving a lasting legacy that transcends time.
The Legacy of the Vikings
The Vikings, a group of seafaring Scandinavian warriors and traders from the late 8th to early 11th centuries, have left an indelible mark on modern culture. Their legacy is not only evident in historical texts but also prominently features in contemporary literature, film, and various forms of popular culture. The portrayal of Vikings has evolved significantly; once depicted purely as barbaric raiders, modern interpretations often highlight their complex society, rich mythology, and contributions to trade and exploration.
In literature, the Norse sagas have served as a crucial source of inspiration, allowing authors and poets to weave tales filled with valor, adventure, and divine interactions. These narratives have influenced a wide array of works, from J.R.R. Tolkien’s epic fantasy realms to Neil Gaiman’s mythological retellings. Additionally, the romanticism surrounding Viking culture can be seen in contemporary novels and stories that focus on their exploration of unknown territories, their adherence to honor codes, and their intricate kinship ties.
The film industry, too, has played a pivotal role in shaping the popular perception of the Vikings. Movies and television series such as “Vikings” have contributed to a renewed interest, often blending historical facts with dramatized storytelling. This has sparked discussions surrounding their image and the distinction between myth and reality, revealing the nuances of Viking life that extend beyond mere conquest.
Archaeological findings continue to enhance our understanding of Viking society, further cementing their legacy. Discoveries of burial sites, artifacts, and thriving settlements illustrate their advancements in shipbuilding and navigation. Such findings challenge earlier misconceptions, emphasizing the Vikings as skilled traders and craftsmen rather than solely ruthless raiders. This evolving narrative underscores the enduring fascination with their culture and the importance of a balanced view of their history, ultimately contributing to the rich tapestry of Scandinavian heritage recognized today.